RSiena (tutorial): Difference between revisions
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
For specifying your model, press specify model on the siena tab. The following dialogue will open. | For specifying your model, press specify model on the siena tab. The following dialogue will open. | ||
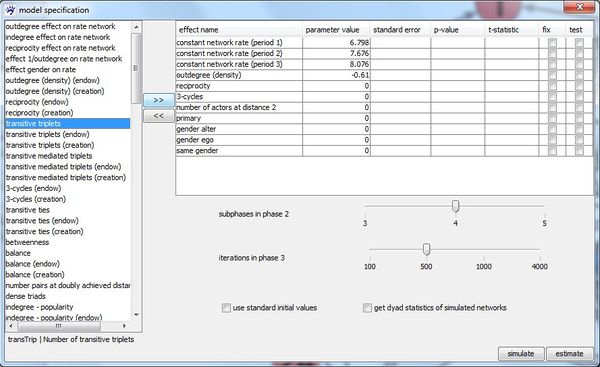
[[File:modelspecification.jpg| | [[File:modelspecification.jpg|600px]] | ||
On the left all | On the left all effects are listed that are available for the active network collection | ||
with the above | with the above specified actor and dyadic attributes. | ||
The right table contains | The right table contains effects that are currently included in the model. Shift effects | ||
from left to right and vice versa to specify your | from left to right and vice versa to specify your effect selection. | ||
For the estimation process, you can choose whether standard values or current parameter | For the estimation process, you can choose whether standard values or current parameter | ||
values shall be used as initial values by ticking the corresponding checkbox. You can | values shall be used as initial values by ticking the corresponding checkbox. You can | ||
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
Parameter estimation starts when button estimate is pressed. The estimation progress | Parameter estimation starts when button estimate is pressed. The estimation progress | ||
can be monitored in the Rserve (see 6) window (console). When the estimation is | can be monitored in the Rserve (see 6) window (console). When the estimation is | ||
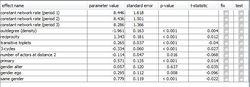
finished, the results are displayed in the right table of the model specification dialogue. | |||
For each included | For each included effect its estimate, associated standard error and t-statistic (that | ||
indicates the convergence of the estimation process, see [1]) are given. The p-values | indicates the convergence of the estimation process, see [1]) are given. The p-values | ||
assume the null hypothesis that respective parameter values are 0 and are calculated by | assume the null hypothesis that respective parameter values are 0 and are calculated by | ||
the R command 2*pnorm(-abs(parameter estimates/standard errors)). | the R command 2*pnorm(-abs(parameter estimates/standard errors)). | ||
It is also possible to test or | It is also possible to test or fix certain effects by ticking the correspondig checkboxes. | ||
When an | When an effect was tested, its p-value results from the score-type test as described in | ||
[1]. | [1]. | ||
When the user closes the model speci�cation dialogue, he has the possibility to save the | When the user closes the model speci�cation dialogue, he has the possibility to save the | ||
Revision as of 10:21, 18 July 2012
This tutorial illustrates how to analyze longitudinal network data by using RSiena from within visone. We assume that you have installed R on your computer and configured the R connection as it is explained in the installation tutorial. We also assume that you have basic understanding about how to work with visone as it is, for instance, explained in the tutorial on visualization and analysis and basic knowledge of stochastic actor-oriented models (SOAM).
To follow the steps illustrated in this tutorial you should download the file Classroom_graphmls.zip and extract (unzip) its content (consisting of the network files classroom_graph1.graphml to classroom_graph4.graphml) to your hard disk. These files constitute the longitudinal network data explained on page Knecht Classroom (data).
Defining longitudinal network data
Stochastic Actor Oriented Models (SAOMs) are designed for analysing longitudinal network data given as network panel data, i.e., a sequence of networks representing one network observed at several moments in time.
Such network panel data are encoded in files classroom_graph1.graphml to classroom_graph4.graphml. To load them click on the menu file, open, navigate in the file browser to the directory where you've put the files classroom_graph1.graphml to classroom_graph4.graphml and select all of them before you click the ok button. (Selection of these files can be done in different ways, for instance, by keeping the Control-key pushed while successively selecting the files with a mouse left-click or by clicking on one of the files and then typing Control-a to select all files in the current directory.)
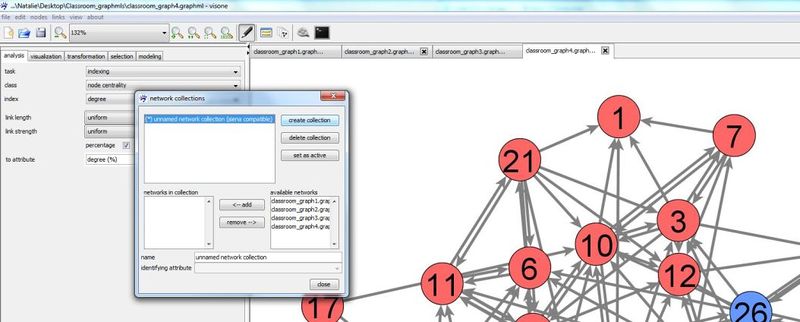
The four networks should be shown in four separate tabs in the network area. However, visone does not yet know that they belong together as a longitudinal network. This information must be given by combining them to a network collection which is a collection or sequence of several networks that belong together, e.g., by building a longitudinal network. Basic application scenarios related to network collections are explained in the tutorial on network collections and dynamic networks.
A network collection can be defined in the network collection manager. To open the network collection manager press button ![]() in visone's toolbar
in visone's toolbar
Press create collection button to create a new collection. A new collection is named 'unknown network collection' by default. You can change the name by clicking in the editable field name and typing a new one.
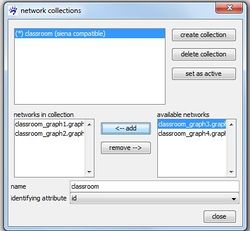
In the right table available networks all networks that can be added to the selected network collection (the selected collection is indicated by the blue background) are listed. These are basically all currently open networks. Select one of them by clicking at its name and press <- add to add it to the seleted collection. The table networks in collection shows you all networks so far contained in the currently selected collection. Note that the top-down order in this table determines the order of the networks in the network collection, hence, has to correspond with their temporal order in the longitudinal network. If the current order is not as you want it, you can rearrange it by removing networks from the collection (clicking at their name and press remove ->) and adding them again which will position them at the very end of the collection.
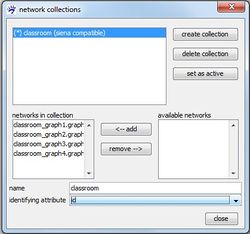
Visone knows now the networks that belong to the collection and their order but it does not know which node in the different networks correspond to each other, i.e., represent the same actor at different moments in time. This information has to be given by specifying an identifying attribute. Candidates for being the identifying attribute are node attributes that are defined in all networks included in the collection. Further they have to be attributes that assign a unique value to each node in a network, i.e., there must not be two nodes in the same network with the same value in those attributes. Among the networks in the network collection nodes with the same value of the identifying attribute are identified with each other.
The drop-down list identifying attribute offers you all available attributes for the current selection that meet the necessary conditions to serve as an identifying attribute. Note that in the current example you are only offered to choose id as the identifying attribute as all other attributes do not provide unique values for all nodes in a network.
While you can create a network collection even if some nodes are not present at all time points, a network collection is marked as being siena compatible if all nodes are present at all times. If a network collection is not siena compatible it cannot be modeled with RSiena but you can nevertheless compute a dynamic layout.
More than one network collection can be created. The analysis with RSiena, however, works on only one longitudinal network data, namely the data represented by the active network collection. At each moment, only one collection can be active which is indicated by the asterisk (*) in front of its name. You can switch the active collection with the set as active button in the collection manager.
Adding individual or dyadic covariates
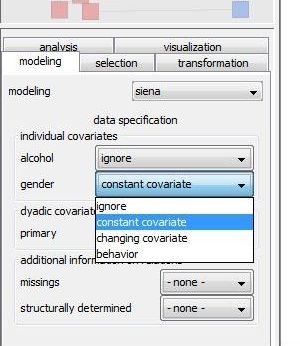
You get to the siena functionalities by choosing on the \texttt{analyis} tab the \texttt{task} "siena". \\ Here, all actor and dyadic attributes that are available for the active network collection (\ref{sec:network_collection}) are listed. Specify for all attributes whether and as which type (e.g., constant or changing covariate) they should be regarded for analysis. The available types for each attribute depend on the sort of data. For instance, a node attribute (\ref{subsec:node_attributes}) that is not integer but decimal, cannot be used as a siena behavior attribute. Also, if a network collection contains only two observations, no node attribute can be used as a changing covariate (see \ref{rs-10} or \ref{ssb-10}).
Specifying missing data or structurally fixed values
Model specification and estimation
For specifying your model, press specify model on the siena tab. The following dialogue will open.
On the left all effects are listed that are available for the active network collection with the above specified actor and dyadic attributes. The right table contains effects that are currently included in the model. Shift effects from left to right and vice versa to specify your effect selection. For the estimation process, you can choose whether standard values or current parameter values shall be used as initial values by ticking the corresponding checkbox. You can also set the number of subphases in phase 2 and the number of iterations in phase 3 (see [1]) by shifting the corresponding sliders.
Parameter estimation starts when button estimate is pressed. The estimation progress can be monitored in the Rserve (see 6) window (console). When the estimation is finished, the results are displayed in the right table of the model specification dialogue. For each included effect its estimate, associated standard error and t-statistic (that indicates the convergence of the estimation process, see [1]) are given. The p-values assume the null hypothesis that respective parameter values are 0 and are calculated by the R command 2*pnorm(-abs(parameter estimates/standard errors)). It is also possible to test or fix certain effects by ticking the correspondig checkboxes. When an effect was tested, its p-value results from the score-type test as described in [1]. When the user closes the model speci�cation dialogue, he has the possibility to save the RSiena output �le. This �le contains the usual RSiena output for estimation results.
Simulation
It is also possible to simulate network evolution. By pressing the simulate button a number of networks is simulated with current parameter estimates. The number of simulations is the number of iterations in phase 3 as set by the user. For each pair of actors the average number of being linked in this simulations is calculated. Resulting tie probabilities are saved as an dyad attribute (5.2) named tie probabilities. When the user closes the model specification dialogue, he has the possibility to save the RSiena output file. This file contains the usual RSiena output for estimation and simulation.