Event networks (tutorial)
Note: this tutorial documents a visone functionality that will be in the next release (around September 2012).
The links in an event network encode time stamped interaction among actors, for instance, users sending emails to other users. There is an important difference to networks of relational states - such as friendship networks. To illustrate the difference, when two actors are friends of each other at some instant in time, then - if nothing happens in between - they are still friends in the very near future. In contrast, if someone sends and email to another person at some instant in time, then he/she does not necessarily send an email to the same person in the very next instant in time.
This tutorial is a practically oriented, example based, "how-to" guide illustrating the import, transformation, visualization, and analysis of event networks with visone. More background on event networks can be found in
- Carter T. Butts: A Relational event framework for social action. Sociological Methodology 38(1):155-200, 2008.
- Ulrik Brandes, Jürgen Lerner, and Tom A. B. Snijders: Networks Evolving Step by Step: Statistical Analysis of Dyadic Event Data. Proc. 2009 Intl. Conf. Advances in Social Network Analysis and Mining (ASONAM 2009), pp.200-205. IEEE Computer Society, 2009.
and in other papers linked in the references.
Example data: networks of political conflict and cooperation
This tutorial uses for illustration networks of events among political actors that have been collected by the Penn State Event Data Project (formerly Kansas Event Data System). Specifically, we use data encoding events in or around the Persian Gulf region in the time from 1979 to 1999. This data set is described in and linked from the page on Penn State Event Data. To follow the steps outlined in this tutorial you should download the file Gulf_events_preprocessed.zip.
Another specific application area for event networks is treated in the tutorial on Wikipedia edit networks.
Importing event data
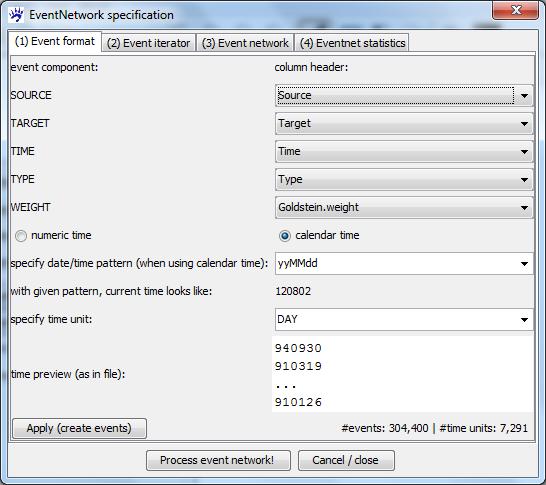
Specifying the event format
References
- Carter T. Butts: A Relational event framework for social action. Sociological Methodology 38(1):155-200, 2008.
- Ulrik Brandes, Jürgen Lerner, and Tom A. B. Snijders: Networks Evolving Step by Step: Statistical Analysis of Dyadic Event Data. Proc. 2009 Intl. Conf. Advances in Social Network Analysis and Mining (ASONAM 2009), pp.200-205. IEEE Computer Society, 2009.